TechTool
» Statics 22
» Statics 21
» Statics 20
» Statics 19
» Statics 18
» Statics 17
» Statics 16
» Statics 15
» Statics 14
» Statics 13
» Statics 12
» Statics 11
» Statics 10
» Statics 9
» Statics 8
» Statics 7
» Statics 6
» Statics 5
» Statics 4
» Statics 3
» Statics 2
» Statics 1

The World of Statistics (1)
By Dr. Magdi Abadir, PhD
Article – 12: Measures of Dispersion (2)
2.2 Quartile deviation
A more credible measure of dispersion that is not affected by the presence of extreme values is the quartile deviation. First, let’s define what are percentiles? Consider the following table showing the scores obtained by 15workers when they were evaluated during a routine performance test (out of 10).| 13 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 15 | 11 |
First, the scores are sorted from smallest to largest:
| 5 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 15 |
Next, two parameters are calculated. The first, known as first quartile, denoted by
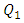 is the number of ranks
is the number of ranks 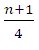 while the second, known as the third quartile denoted by
while the second, known as the third quartile denoted by 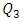 is the number of ranks
is the number of ranks 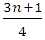 (Where n is the total number of data). The quartile deviation is defined by
(Where n is the total number of data). The quartile deviation is defined by 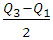
In the previous set of data, since n=15, then
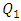 will be the number of ranks
will be the number of ranks 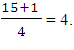 The 4th number in the set is 9.
The 4th number in the set is 9. 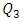 will be the number of ranks
will be the number of ranks 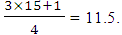 The 11th number in the set is 12, and the 12th is 13. The value of
The 11th number in the set is 12, and the 12th is 13. The value of 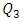 is taken as the average of these two numbers, namely 12.5.
Therefore, the quartile deviation
is taken as the average of these two numbers, namely 12.5.
Therefore, the quartile deviation 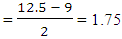
If the smallest and largest score were discarded, then
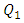 will be the number of ranks
will be the number of ranks 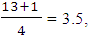 which is taken as the mean between the 2nd and 3rd numbers = 8.5. Also,
which is taken as the mean between the 2nd and 3rd numbers = 8.5. Also, 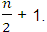 will be the number of ranks
will be the number of ranks 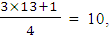 which is the number 12. The quartile deviation in that case
which is the number 12. The quartile deviation in that case 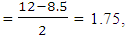 a value identical to that obtained when the two outliers (5 and 15) were included. This simple example reveals the merit of using the quartile deviation over the range as measure of dispersion as far as the effect of outliers is concerned.
However, the quartile deviation suffers from some demerits that can be summarized in the following points:
a value identical to that obtained when the two outliers (5 and 15) were included. This simple example reveals the merit of using the quartile deviation over the range as measure of dispersion as far as the effect of outliers is concerned.
However, the quartile deviation suffers from some demerits that can be summarized in the following points:
- It is not based on all the observations of a series but rather on 2 figures only.
- It is affected by fluctuations in sampling in case of large populations.
- It does not exhibit any scatter around an average for which is remarked as a measure of partition rather than a measure of dispersion.
References:
(1) Manikandan S. (2011) "Measures of dispersion" J. Pharmacol Pharmacother 2(4): 315 - 316
| Dr. Magdi Fouad Abadir, Ph. D.: Dr. M. F. Abadir is currently a professor with the Chemical Engineering Department at the Faculty of Engineering, University of Cairo, Egypt. His major interests are in the fields of high temperature science and technology. During his career, he has supervised more than 110 MSc and PhD theses and published more than a hundred papers mostly in international peer review journals. He currently teaches courses in High Temperature Technology and Industrial Statistics. He is also a consultant for several industrial businesses. |




